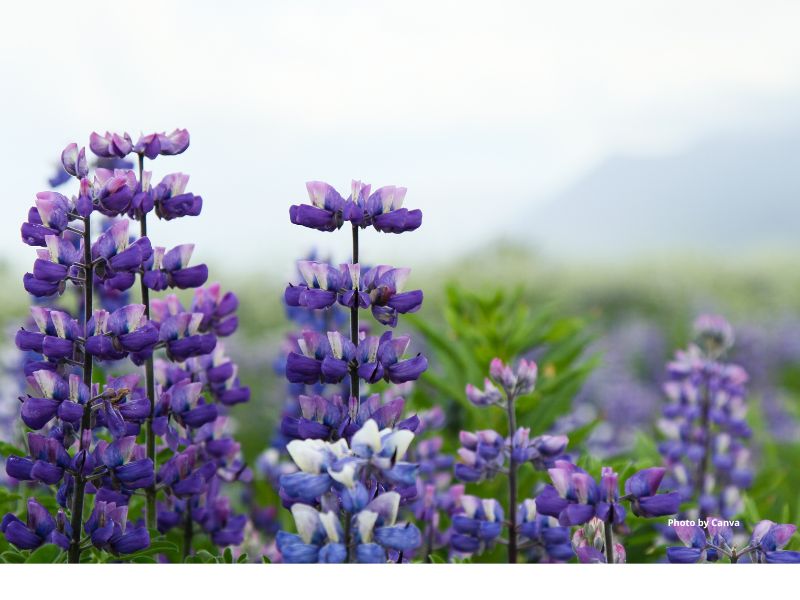
Nootka Lupine
Lupinus nootkatensis
Appearance
range & habitat
reciprocal relationships
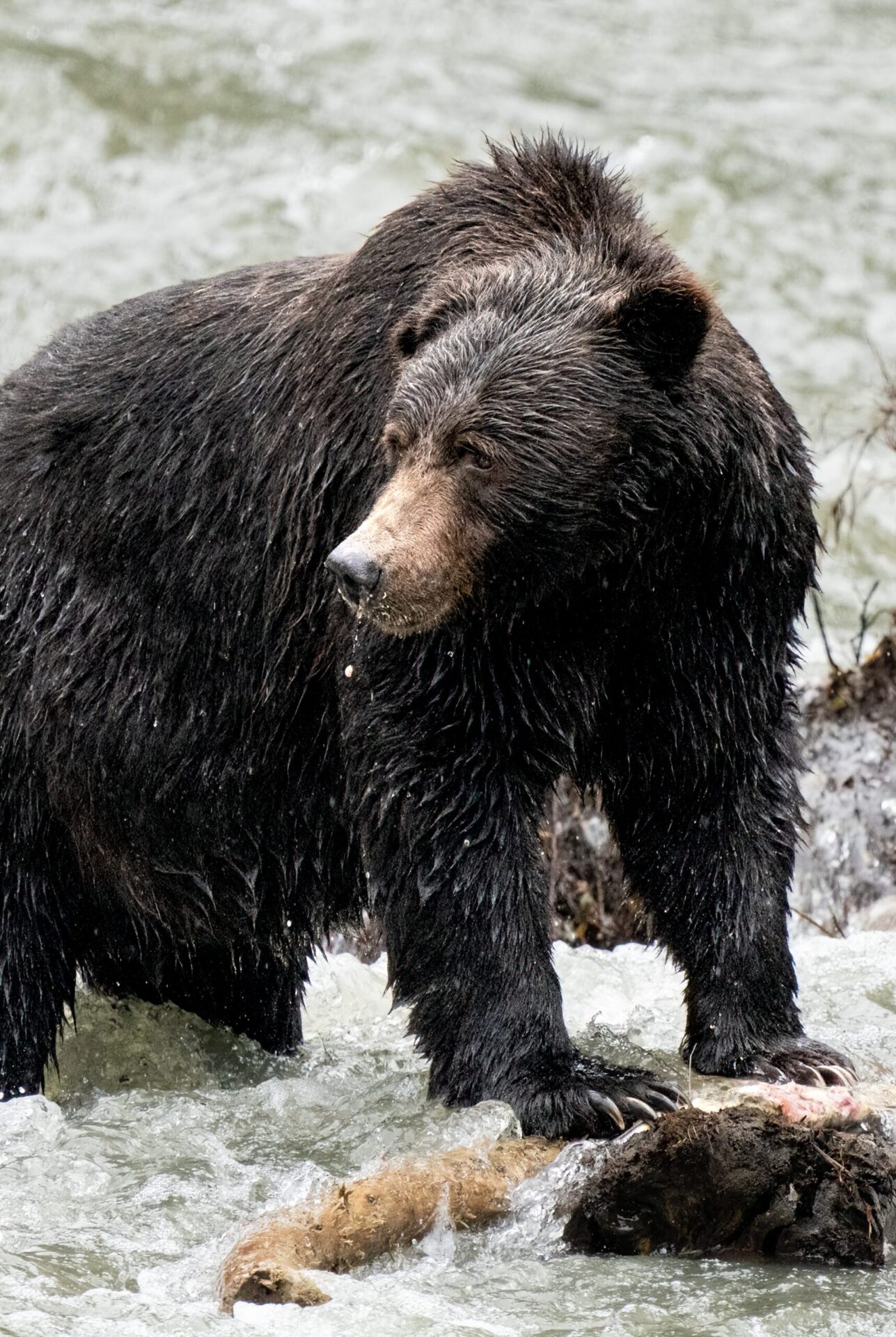
Bears love to eat the roots of Nootka lupine.
Some butterflies feed off the lupine and lay their eggs on its leaves. The roots are roasted by the Nuxalk and Kwakwaka’wak. The seeds should not be consumed as they are poisonous, especially in large quantities.