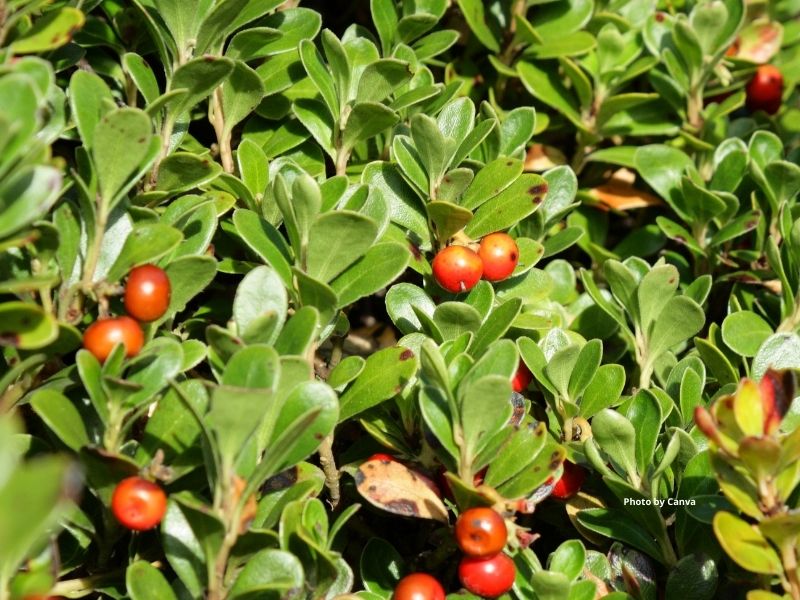
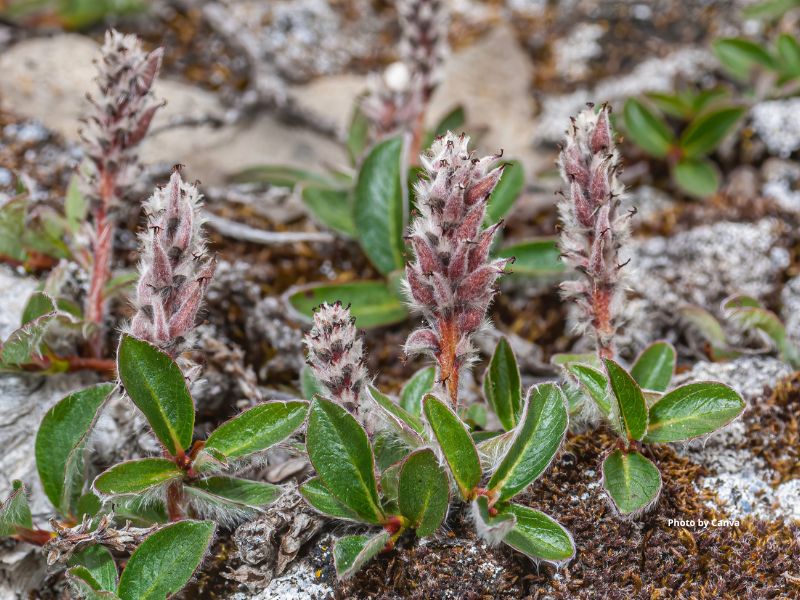
Kinnikinnick (Common Bearberry)
Arctostaphylos uva-ursi
APPEARANCE
RANGE & HABITAT
RECIPORCAL RELATIONSHIPS
Kinnikinnick comes from an Algonquin word meaning mixed. This is because it used to refer to a mix of other plants that was smoked in various ceremonies. The plant kinnikinnick can also be made into yummy tea with an almond flavour. In Sweden and Russia, the tannins in the leaves have been used for tanning leather.