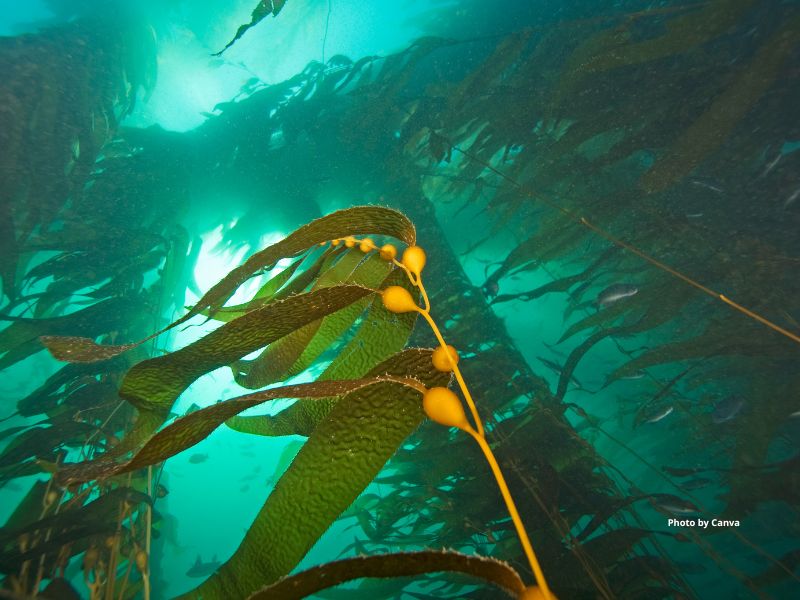
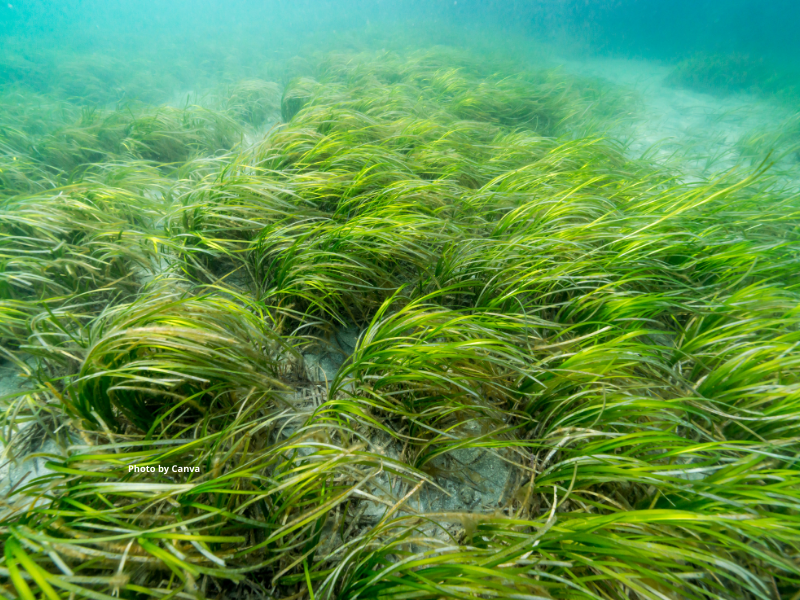
Kelp
Laminariales
Appearance
Range & habitat
In general, kelp thrive in rocky areas near the shoreline, where there are lots of nutrients, cold seawater, and calm waves. Kelp is found in oceans all around the world!
reciprocal relationships
Ocean kelp plays a critically important role in B.C.’s marine ecosystems. As a primary producer, it is responsible for producing much of the plant material that other species higher in the food web depend on.
Young fish use kelp to grow and develop. Sea otters and seals frequently hang out around kelp forests because of the wide selection of food available. Over 150 different species are known to live in kelp forests, including crabs, sea stars, and octopuses. Kelp forests are among the most diverse and productive ecosystems in the entire world!
Every year, kelp plants die in the winter and are replaced by new plants in the spring. Decaying kelp provides food and shelter for small coastal insects.
Kelp bulbs and hollow stipes are cured and used to store seal oil. The solid part of the stem can be used as fish lines after being soaked in fresh water, stretched and twisted for extra strength. Nets, ropes, harpoon lines and anchor lines can also be made from kelp. Coastal peoples have long relied on hunting animals that live within kelp beds, such as fish, shellfish, seals and otters. The Kitasoo and Xai’xais people settled in Klemtu thousands of years ago due to the abundance of kelp in the bay.
status
Climate change also poses a risk to these precious kelp forests due to the changes in ocean temperature and nutrients that accompany it.
COSEWIC: Not Reported
CDC: Not Reported